| THE WORLDWIDE VEGETABLES |
|
FAMILY BRASSICACEAE
CRUCIFERS OR CABBAGE FAMILY
Edited by Ho Dinh Hai
Long An - Vietnam
Updated: 20/3/2015
1- Introduction to the Family Brassicaceae
1.1- Overview
+ The Family Brassicaceae
The Brassicaceae, a medium-sized and economically important family of flowering plants (Angiosperms), are informally known as the mustards, mustard flowers, the crucifers or the cabbage family.
The name Brassicaceae is derived from the included genus Brassica. Cruciferae, an older name, meaning "cross-bearing", describes the four petals of mustard flowers, which are reminiscent of a cross; it is one of eight plant family names without the suffix '-aceae' that are authorized alternative names (according to ICBN Art. 18.5 and 18.6 Vienna Code), thus both Cruciferae and Brassicaceae are used.
The family contains well-known species such as Brassica oleracea (broccoli, cabbage, cauliflower, etc.), Brassica rapa (turnip, Chinese cabbage, etc.), Brassica napus (rapeseed, etc.), Raphanus sativus (common radish), Armoracia rusticana (horseradish), Matthiola (stock), Arabidopsis thaliana (thale cress) (model organism) and many others.
Pieris rapae and other butterflies of the Pieridae family are some of the most well known pests of the commercial cropping of Brassicaceae.
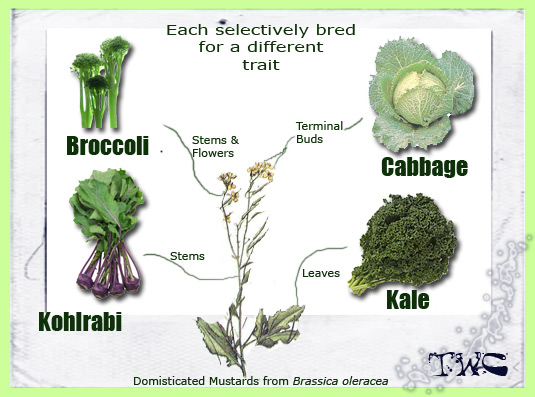
The importance of this family for food crops has led to its selective breeding throughout history. Some examples of cruciferous food plants are the cabbage, broccoli, cauliflower, turnip, rapeseed, mustard, radish, horseradish, cress, wasabi, and watercress.
+ Cruciferous Vegetables
Cruciferous vegetables are vegetables of the family Brassicaceae (also called Cruciferae). These vegetables are widely cultivated, with many genera, species, and cultivars being raised for food production such as cauliflower, cabbage, garden cress, bok choy, broccoli, brussels sprouts and similar green leaf vegetables. The family takes its alternate name (Cruciferae, New Latin for "cross-bearing") from the shape of their flowers, whose four petals resemble a cross.
Ten of the most common cruciferous vegetables eaten by people, known colloquially as cole crops, are in a single species (Brassica oleracea); they are not distinguished from one another taxonomically, only by horticultural category of cultivar groups. Numerous other genera and species in the family are also edible. Cruciferous vegetables are one of the dominant food crops worldwide. They are high in vitamin C and soluble fiber and contain multiple nutrients and phytochemicals.
1.2- The names of Family Brassicaceae
The name Brassicaceae is derived from the included genus Brassica. Cruciferae, an older name, meaning "cross-bearing", describes the four petals of mustard flowers, which are reminiscent of a cross; it is one of eight plant family names without the suffix '-aceae' that are authorized alternative names (according to ICBN Art. 18.5 and 18.6 Vienna Code), thus both Cruciferae and Brassicaceae are used.
+ The Family Brassicaceae
The Brassicaceae, a medium-sized and economically important family of flowering plants (Angiosperms), are informally known as the mustards, mustard flowers, the crucifers or the cabbage family.
The name Brassicaceae is derived from the included genus Brassica. Cruciferae, an older name, meaning "cross-bearing", describes the four petals of mustard flowers, which are reminiscent of a cross; it is one of eight plant family names without the suffix '-aceae' that are authorized alternative names (according to ICBN Art. 18.5 and 18.6 Vienna Code), thus both Cruciferae and Brassicaceae are used.
The family contains well-known species such as Brassica oleracea (broccoli, cabbage, cauliflower, etc.), Brassica rapa (turnip, Chinese cabbage, etc.), Brassica napus (rapeseed, etc.), Raphanus sativus (common radish), Armoracia rusticana (horseradish), Matthiola (stock), Arabidopsis thaliana (thale cress) (model organism) and many others.
Pieris rapae and other butterflies of the Pieridae family are some of the most well known pests of the commercial cropping of Brassicaceae.
The importance of this family for food crops has led to its selective breeding throughout history. Some examples of cruciferous food plants are the cabbage, broccoli, cauliflower, turnip, rapeseed, mustard, radish, horseradish, cress, wasabi, and watercress.
+ Cruciferous Vegetables
Cruciferous vegetables are vegetables of the family Brassicaceae (also called Cruciferae). These vegetables are widely cultivated, with many genera, species, and cultivars being raised for food production such as cauliflower, cabbage, garden cress, bok choy, broccoli, brussels sprouts and similar green leaf vegetables. The family takes its alternate name (Cruciferae, New Latin for "cross-bearing") from the shape of their flowers, whose four petals resemble a cross.
Ten of the most common cruciferous vegetables eaten by people, known colloquially as cole crops, are in a single species (Brassica oleracea); they are not distinguished from one another taxonomically, only by horticultural category of cultivar groups. Numerous other genera and species in the family are also edible. Cruciferous vegetables are one of the dominant food crops worldwide. They are high in vitamin C and soluble fiber and contain multiple nutrients and phytochemicals.
1.2- The names of Family Brassicaceae
The name Brassicaceae is derived from the included genus Brassica. Cruciferae, an older name, meaning "cross-bearing", describes the four petals of mustard flowers, which are reminiscent of a cross; it is one of eight plant family names without the suffix '-aceae' that are authorized alternative names (according to ICBN Art. 18.5 and 18.6 Vienna Code), thus both Cruciferae and Brassicaceae are used.
1.3- Characteristics
The family consists mostly of herbaceous plants with annual, biennial or perennial lifespans. However, around the Mediterranean they include also a dozen woody shrubs 1m - 3m tall, e.g. in northern Africa (Zilla spinosa and Ptilotrichum spinosum), in the Dalmatian islands (Dendralyssum and Cramboxylon), and chiefly in Canarias with some woody cruciferous genera: Dendrosinapis, Descurainia, Parolinia, Stanleya, etc..
The leaves are alternate (rarely opposite), sometimes organized in basal rosettes; in rare shrubby crucifers of Mediterranean their leaves are mostly in terminal rosettes, and may be coriaceous and evergreen. They are very often pinnately incised and do not have stipules.
The structure of the flowers is extremely uniform throughout the family. They have four free saccate sepals and four clawed free petals, staggered. They can be disymmetric or slightly zygomorphic, with a typical cross-like arrangement (hence the name 'Cruciferae'). They have six stamens, four of which are longer (as long as the petals, so relatively short in fact) and are arranged in a cross like the petals and the other two are shorter (tetradynamous flower). The pistil is made up of two fused carpels and the style is very short, with two lobes. Superior ovary. The flowers form ebracteate racemose inflorescences, often apically corymb-like.
Pollination occurs by entomogamy, nectar is produced at the base of the stamens and stored on the sepals.
The fruit is a peculiar kind of capsule named siliqua (plural siliquae, American English silique/siliques). It opens by two valves, which are the modified carpels, leaving the seeds attached to a framework made up of the placenta and tissue from the junction between the valves (replum). There is often an indehiscent beak at the top of the style and one or more seeds may be borne there. Where a siliqua is less than three times as long as it is broad, it is usually termed a silicula. The siliqua may break apart at constrictions occurring between the segments of the seeds, thus forming a sort of loment (e.g., Raphanus), it may eject the seeds explosively (e.g., Cardamine) or may be evolved in a sort of samara (e.g., Isatis). The fruit is often the most important diagnostic character for plants in this family.
Brassicaceae do not form mycorrhizae, although rare exceptions do exist.
Most members share a suite of glucosinolate compounds that have a typical pungent odour usually associated with cole crops.
The family consists mostly of herbaceous plants with annual, biennial or perennial lifespans. However, around the Mediterranean they include also a dozen woody shrubs 1m - 3m tall, e.g. in northern Africa (Zilla spinosa and Ptilotrichum spinosum), in the Dalmatian islands (Dendralyssum and Cramboxylon), and chiefly in Canarias with some woody cruciferous genera: Dendrosinapis, Descurainia, Parolinia, Stanleya, etc..
The leaves are alternate (rarely opposite), sometimes organized in basal rosettes; in rare shrubby crucifers of Mediterranean their leaves are mostly in terminal rosettes, and may be coriaceous and evergreen. They are very often pinnately incised and do not have stipules.
The structure of the flowers is extremely uniform throughout the family. They have four free saccate sepals and four clawed free petals, staggered. They can be disymmetric or slightly zygomorphic, with a typical cross-like arrangement (hence the name 'Cruciferae'). They have six stamens, four of which are longer (as long as the petals, so relatively short in fact) and are arranged in a cross like the petals and the other two are shorter (tetradynamous flower). The pistil is made up of two fused carpels and the style is very short, with two lobes. Superior ovary. The flowers form ebracteate racemose inflorescences, often apically corymb-like.
Pollination occurs by entomogamy, nectar is produced at the base of the stamens and stored on the sepals.
The fruit is a peculiar kind of capsule named siliqua (plural siliquae, American English silique/siliques). It opens by two valves, which are the modified carpels, leaving the seeds attached to a framework made up of the placenta and tissue from the junction between the valves (replum). There is often an indehiscent beak at the top of the style and one or more seeds may be borne there. Where a siliqua is less than three times as long as it is broad, it is usually termed a silicula. The siliqua may break apart at constrictions occurring between the segments of the seeds, thus forming a sort of loment (e.g., Raphanus), it may eject the seeds explosively (e.g., Cardamine) or may be evolved in a sort of samara (e.g., Isatis). The fruit is often the most important diagnostic character for plants in this family.
Brassicaceae do not form mycorrhizae, although rare exceptions do exist.
Most members share a suite of glucosinolate compounds that have a typical pungent odour usually associated with cole crops.
1.4- The Uses of Cruciferous vegetables
The importance of this family for food crops has led to its selective breeding throughout history. Some examples of cruciferous food plants are the cabbage, broccoli, cauliflower, turnip, rapeseed, mustard, radish, horseradish, cress, wasabi, and watercress.
Matthiola (stock), Cheiranthus, Lobularia and Iberis (candytufts) are appreciated for their flowers. Lunaria (honesty) is cultivated for the decorative value of the translucent replum of the round silicula that remains on the dried stems after dehiscence.
Capsella bursa-pastoris, Lepidium, and many Cardamine are common weeds.
Isatis tinctoria (woad) was used in the past to produce the colour indigo.
Arabidopsis thaliana is a very important model organism in the study of the flowering plants (Angiospermae).
The importance of this family for food crops has led to its selective breeding throughout history. Some examples of cruciferous food plants are the cabbage, broccoli, cauliflower, turnip, rapeseed, mustard, radish, horseradish, cress, wasabi, and watercress.
Matthiola (stock), Cheiranthus, Lobularia and Iberis (candytufts) are appreciated for their flowers. Lunaria (honesty) is cultivated for the decorative value of the translucent replum of the round silicula that remains on the dried stems after dehiscence.
Capsella bursa-pastoris, Lepidium, and many Cardamine are common weeds.
Isatis tinctoria (woad) was used in the past to produce the colour indigo.
Arabidopsis thaliana is a very important model organism in the study of the flowering plants (Angiospermae).
2- Taxonomy of the Family Brassicaceae
2.1- Overview
The family contains over 330 genera and about 3,700 species, according to the Royal Botanic Gardens, Kew. The largest genera are Draba (365 species), Cardamine (200 species, but its definition is controversial), Erysimum (225 species), Lepidium (230 species), and Alyssum (195 species).
The family is included in Brassicales according to the APG system. This family comprises about 365 genera and 3200 species all over the world. The plants are mostly herbs.
A close relationship has long been acknowledged between Brassicaceae and the caper family, Capparaceae, in part because members of both groups produce glucosinolate (mustard oil) compounds. Recent research (Hall et al. 2002) suggests that Capparaceae as traditionally circumscribed are paraphyletic with respect to Brassicaceae, with Cleome and several related genera being more closely related to Brassicaceae than to other Capparaceae.
The APG II system, therefore, has merged the two families under the name 'Brassicaceae'. Other classifications have continued to recognize Capparaceae but with a more restricted circumscription, either including Cleome and its relatives in Brassicaceae or recognizing them in the segregate family Cleomaceae.
The APG III system has recently adopted this last solution, but this may change as a consensus arises on this point. This article deals with Brassicaceae sensu stricto, i.e. treating Cleomaceae and Capparaceae as segregate families.
Older systems (e.g., Arthur Cronquist's) placed them into the Capparales, a now-defunct order that had a similar definition.
The family contains over 330 genera and about 3,700 species, according to the Royal Botanic Gardens, Kew. The largest genera are Draba (365 species), Cardamine (200 species, but its definition is controversial), Erysimum (225 species), Lepidium (230 species), and Alyssum (195 species).
The family is included in Brassicales according to the APG system. This family comprises about 365 genera and 3200 species all over the world. The plants are mostly herbs.
A close relationship has long been acknowledged between Brassicaceae and the caper family, Capparaceae, in part because members of both groups produce glucosinolate (mustard oil) compounds. Recent research (Hall et al. 2002) suggests that Capparaceae as traditionally circumscribed are paraphyletic with respect to Brassicaceae, with Cleome and several related genera being more closely related to Brassicaceae than to other Capparaceae.
The APG II system, therefore, has merged the two families under the name 'Brassicaceae'. Other classifications have continued to recognize Capparaceae but with a more restricted circumscription, either including Cleome and its relatives in Brassicaceae or recognizing them in the segregate family Cleomaceae.
The APG III system has recently adopted this last solution, but this may change as a consensus arises on this point. This article deals with Brassicaceae sensu stricto, i.e. treating Cleomaceae and Capparaceae as segregate families.
Older systems (e.g., Arthur Cronquist's) placed them into the Capparales, a now-defunct order that had a similar definition.
2.2- Taxonomy depending on The APG III system (2009)
+ Family Brassicaceae
Brassicaceae is a large and complex family of considerable economic importance to humans. It is most highly diversified in central and western Asia, Mediterranean Europe and western North America.
The family is included in Brassicales according to the APG system. This family comprises about 365 genera and 3200 species all over the world. The plants are mostly herbs.
+ Tribes of Family Brassicaceae
The National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. (NCBI) advances science and health by providing access to biomedical and genomic information. It includes the list of tribes of family Brassicaceae as the following:
Included tribes (for NCBI, 8 April 2014):
+ Family Brassicaceae
Brassicaceae is a large and complex family of considerable economic importance to humans. It is most highly diversified in central and western Asia, Mediterranean Europe and western North America.
The family is included in Brassicales according to the APG system. This family comprises about 365 genera and 3200 species all over the world. The plants are mostly herbs.
+ Tribes of Family Brassicaceae
The National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. (NCBI) advances science and health by providing access to biomedical and genomic information. It includes the list of tribes of family Brassicaceae as the following:
Included tribes (for NCBI, 8 April 2014):
|
1- Aethionemeae,
2- Alysseae, 3- Alyssopsideae, 4- Anastaticeae, 5- Anchonieae, 6- Aphragmeae, 7- Arabideae, 8- Asteae, 9- Biscutelleae, 10- Bivonaeeae, 11- Boechereae, 12- Brassiceae, 13- Buniadeae, 14- Calepineae, 15- Camelineae, 16- Cardamineae, 17- Chorisporeae, 18- Cochlearieae, 19- Coluteocarpeae. |
20- Conringieae,
21- Cremolobeae, 22- Crucihimalayeae, 23- Descurainieae, 24- Dontostemoneae, 25- Erysimeae, 26- Euclidieae, 27- Eudemeae, 28- Eutremeae, 29- Halimolobeae, 30- Heliophileae, 31- Hesperideae, 32- Iberideae, 33- Isatideae, 34- Kernereae, 35- Lepidieae, 36- Malcolmieae, 37- Megacarpaeeae, 38- Microlepidieae. |
39- Lepidieae,
40- Malcolmieae, 41- Megacarpaeeae, 42- Microlepidieae, 43- Noccaeeae, 44- Notothlaspideae, 45- Oreophytoneae, 46- Physarieae, 47- Schizopetaleae, 48- Scoliaxoneae, 49- Sisymbrieae, 50- Smelowskieae, 51- Stevenieae, 52- Thelypodieae, 53- Thlaspideae, 54- Turritideae, 55- Yinshanieae, 56- Brassicaceae incertae sedis. - |
3- The Important Genera of Common cruciferous vegetables
3.1- Genus Armoracia
1- Armoracia rusticana - Horseradish
3.2- Genus Barbarea
2- Barbarea verna - Land cress
3.3- Genus Brassica
3- Brassica carinata - Ethiopian mustard
4- Brassica oleracea - Kale: Acephala group
5- Brassica oleracea- Collard greens: Acephala Group
6- Brassica oleracea - Chinese broccoli (gai-lan): Alboglabra Group
7- Brassica oleracea- Cauliflower: Botrytis Group
8- Brassica oleracea - Cabbage: Capitata Group
9- Brassica oleracea - Broccoli romanesco: Botrytis Group / Italica Group
10- Brassica oleracea - Brussels sprouts: Gemmifera Group
11- Brassica oleracea - Kohlrabi: Gongylodes Group
12- Brassica oleracea - Broccoli: Italica Group
13- Brassica oleracea - Broccoflower: Italica Group × Botrytis Group
14- Brassica oleracea - Wild broccoli: Oleracea Group
15- Brassica oleracea - Savoy cabbage: Savoy Cabbage Group
16- Brassica rapa - Komatsuna: pervidis or komatsuna
17- Brassica rapa var. chinensis - Bok choy
18- Brassica rapa var. Nipposinica - Mizuna
19- Brassica rapa var. parachinensis - Rapini (broccoli rabe)
20- Brassica rapa var. parachinensis - Flowering cabbage
21- Brassica rapa var. pekinensis - Chinese cabbage, napa cabbage
22- Brassica rapa var. rapifera - Turnip root; greens
23- Brassica napus var. napobrassica - Rutabaga (swede)
24- Brassica napus var. pabularia - Siberian kale
25- Brassica rapa/napus var. oleifera - Canola/rapeseed
26- Brassica juncea - Mustard seeds, brown; greens
27- Brassica juncea var. rugosa - Wrapped heart mustard cabbage
28- Brassica (or Sinapis) hirta - White mustard seeds
29- Brassica nigra - Black mustard seeds
30- Brassica rosularis - Tatsoi
3.4- Genus Diolotaxis
31- Diplotaxis tenuifolia - Wild arugula
3.5- Genus Eruca
32- Eruca vesicaria - Arugula (rocket)
3.6- Genus Lepidium
33- Lepidium campestre - Field pepperweed
34- Lepidium meyenii - Maca
35- Lepidium sativum - Garden cress
3.7- Genus Raphanus
36- Raphanus sativus var. longipinnatus - Daikon
3.8- Genus Nasturtium
37- Nasturtium officinale - Watercress
3.9- Genus Raphanus
38- Raphanus sativus - Radish
3.10- Genus Wasabia
39- Wasabia japonica - Wasabi
Source: Cruciferous vegetables - From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Cruciferous_vegetables.
1- Armoracia rusticana - Horseradish
3.2- Genus Barbarea
2- Barbarea verna - Land cress
3.3- Genus Brassica
3- Brassica carinata - Ethiopian mustard
4- Brassica oleracea - Kale: Acephala group
5- Brassica oleracea- Collard greens: Acephala Group
6- Brassica oleracea - Chinese broccoli (gai-lan): Alboglabra Group
7- Brassica oleracea- Cauliflower: Botrytis Group
8- Brassica oleracea - Cabbage: Capitata Group
9- Brassica oleracea - Broccoli romanesco: Botrytis Group / Italica Group
10- Brassica oleracea - Brussels sprouts: Gemmifera Group
11- Brassica oleracea - Kohlrabi: Gongylodes Group
12- Brassica oleracea - Broccoli: Italica Group
13- Brassica oleracea - Broccoflower: Italica Group × Botrytis Group
14- Brassica oleracea - Wild broccoli: Oleracea Group
15- Brassica oleracea - Savoy cabbage: Savoy Cabbage Group
16- Brassica rapa - Komatsuna: pervidis or komatsuna
17- Brassica rapa var. chinensis - Bok choy
18- Brassica rapa var. Nipposinica - Mizuna
19- Brassica rapa var. parachinensis - Rapini (broccoli rabe)
20- Brassica rapa var. parachinensis - Flowering cabbage
21- Brassica rapa var. pekinensis - Chinese cabbage, napa cabbage
22- Brassica rapa var. rapifera - Turnip root; greens
23- Brassica napus var. napobrassica - Rutabaga (swede)
24- Brassica napus var. pabularia - Siberian kale
25- Brassica rapa/napus var. oleifera - Canola/rapeseed
26- Brassica juncea - Mustard seeds, brown; greens
27- Brassica juncea var. rugosa - Wrapped heart mustard cabbage
28- Brassica (or Sinapis) hirta - White mustard seeds
29- Brassica nigra - Black mustard seeds
30- Brassica rosularis - Tatsoi
3.4- Genus Diolotaxis
31- Diplotaxis tenuifolia - Wild arugula
3.5- Genus Eruca
32- Eruca vesicaria - Arugula (rocket)
3.6- Genus Lepidium
33- Lepidium campestre - Field pepperweed
34- Lepidium meyenii - Maca
35- Lepidium sativum - Garden cress
3.7- Genus Raphanus
36- Raphanus sativus var. longipinnatus - Daikon
3.8- Genus Nasturtium
37- Nasturtium officinale - Watercress
3.9- Genus Raphanus
38- Raphanus sativus - Radish
3.10- Genus Wasabia
39- Wasabia japonica - Wasabi
Source: Cruciferous vegetables - From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Cruciferous_vegetables.
Edited by Ho Dinh Hai
Long An – Vietnam
References
1- http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Brassicales
2- http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Brassicaceae
3- http://theworldwidevegetables.weebly.com/order-brassicales.html
4- http://www.britannica.com/plant/Brassicaceae
5- https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/Category:Brassicaceae
6- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Cruciferous_vegetables.
7- https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/Category:Brassiceae
8- http://flora.huh.harvard.edu/Brassicaceae
9- http://flora.huh.harvard.edu/Brassicaceae/intkey/WWW/Genera.htm
See Video about: Family Brassicaceae
Long An – Vietnam
References
1- http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Brassicales
2- http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Brassicaceae
3- http://theworldwidevegetables.weebly.com/order-brassicales.html
4- http://www.britannica.com/plant/Brassicaceae
5- https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/Category:Brassicaceae
6- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Cruciferous_vegetables.
7- https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/Category:Brassiceae
8- http://flora.huh.harvard.edu/Brassicaceae
9- http://flora.huh.harvard.edu/Brassicaceae/intkey/WWW/Genera.htm
See Video about: Family Brassicaceae
See Video about: Raw Cruciferous Vegetables and Thyroid Health-My Personal Case History.